Innovation is often the key to unlocking life-changing treatments — particularly when it comes to rare diseases.
Yet, getting a novel therapy to market for rare conditions can be a complex journey with regulatory hurdles, limited patient populations and significant development costs.
Obtaining orphan drug designation (ODD) is a crucial step if you're a biotech or pharma company looking to develop therapies for rare diseases. But what does navigating orphan drug designation really mean for your clinical research, and how can your organisation ensure a successful application?
In this blog, we'll break down the orphan drug designation process, explain its importance and share key strategies to help your team successfully navigate the regulatory landscape for rare diseases.
Understanding orphan drug designation
Orphan drug designation is a special status granted by regulatory agencies such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) to encourage drug development for rare diseases.
Obtaining orphan drug status offers several key benefits, including:
- Reduced development costs. Tax credits for clinical trials can significantly reduce the cost burden, making developing rare disease therapies more financially feasible for you, especially if you're a smaller biotech or pharmaceutical company.
- Market exclusivity (usually seven years in the US and 10 years in the EU). With a guaranteed period of exclusivity, your drug can dominate the market without competition for several years, ensuring higher revenue potential.
- Faster approval process. Orphan drug designation often leads to expedited development programmes, increasing the chances of your drug reaching the market sooner.
- Attracting investment. The incentives and credibility associated with orphan drug status can make your company more attractive to investors who are keen to fund innovative therapies in niche markets.
However, while these incentives sound attractive, the application process for orphan drug status is highly specific and requires deep expertise in regulatory affairs, clinical development and rare disease modelling.
The challenges of obtaining orphan drug designation
While the benefits of orphan drug designation are clear, there are four key challenges you must address during the process.
- Understanding the regulatory landscape. Each region has its own regulations regarding orphan drugs. Navigating both the FDA and EMA ODD requirements can be a significant challenge, especially when pursuing global development.
- Demonstrating the 'rare' nature of the disease. To qualify for ODD, the disease must meet the criteria for rarity; proving this can sometimes be challenging. In certain cases, clinical data might be limited, which complicates efforts to show the true scope and impact of the disease.
- Clinical trial design and data. Conducting clinical trials for rare diseases often involves small patient populations, leading to challenges in statistical power and generalisability. Additionally, orphan drug clinical trials can be costly due to the complexities involved.
- Access to funding. Although ODD offers tax credits and grants, securing sufficient funding for clinical development can still be an obstacle. The development of orphan drugs is expensive, and the market size is often too small to justify traditional investment models.
How to navigate your orphan drug designation application successfully
If you want to bring an orphan drug to market, you should consider these five points as part of your strategy and application process.
- Early engagement with regulatory authorities. Proactive communication with regulatory agencies is key. Pre-IND (investigational new drug) meetings with the FDA or equivalent meetings with the EMA can help clarify orphan drug designation criteria and ensure your application is well-supported with the appropriate clinical data.
- Leveraging real-world data and patient registries. While traditional clinical trials for rare diseases can be limited, using real-world data and patient registries can support the case for orphan drug designation. These resources help to demonstrate disease prevalence, patient outcomes and treatment gaps, offering valuable evidence for regulatory agencies.
- Designing adaptive trials. Adaptive clinical trial designs, which allow modifications to the trial as it progresses based on interim results, are particularly well-suited for rare diseases. This approach maximises efficiency by minimising unnecessary trials and increasing the likelihood of success.
- Global strategy alignment. In a world of global health crises and multinational collaboration, understanding the global regulatory landscape is essential. Aligning orphan drug designation efforts across key regions (e.g. the US, Europe and Japan) can streamline development and improve the chances of approval in multiple markets.
- Building strong collaborations. Working with patient advocacy groups, disease experts and other stakeholders can provide essential support for orphan drug designation applications. Collaboration helps strengthen your application with patient testimonials, additional data and enhanced credibility.
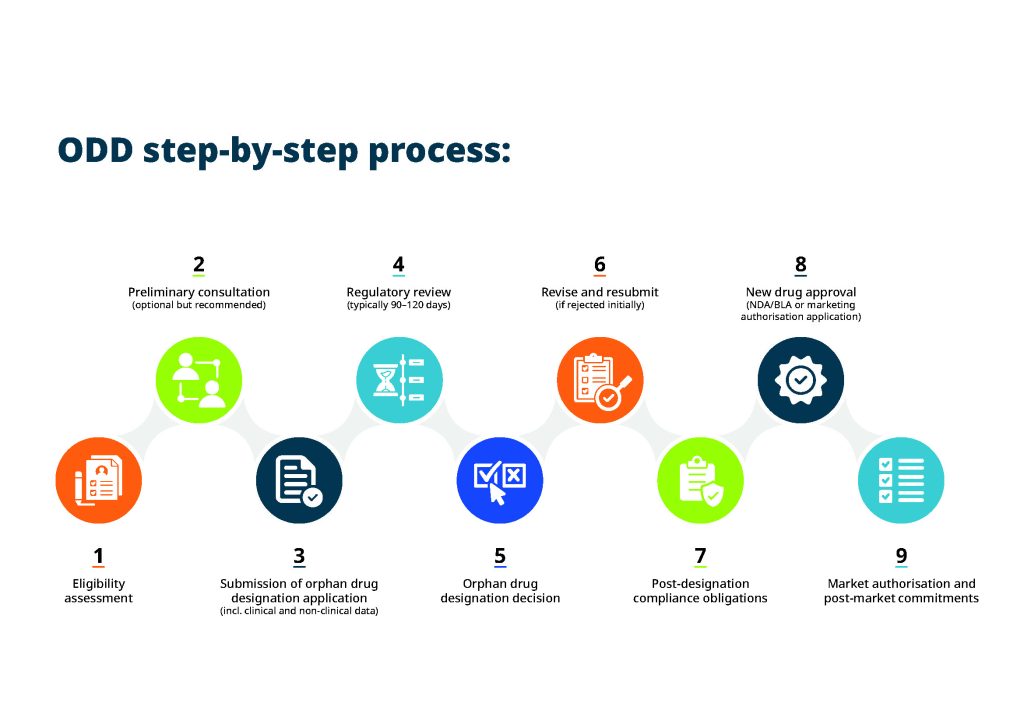
Support your marketing authorisation application and gain ODD status
Navigating orphan drug designation for rare diseases is undoubtedly challenging but also incredibly rewarding. The benefits it provides — ranging from tax incentives to faster market access — are invaluable.
By approaching the ODD process strategically, you significantly improve your chances of developing breakthrough therapies for rare diseases and making a lasting impact in the lives of patients who need it most. TMC's pharma consulting services support your orphan drug designation to help you move through your drug development timeline quickly, compliantly and cost-effectively.
Find out more about TMC Consulting or contact our team today at connect@tmcpharma.com to help you gain ODD status with the FDA or EMA.
